Businesses use the sensitivity analysis mental model to make tough decisions when outcomes feel unpredictable? Imagine tweaking one factor in a financial plan and instantly seeing how it ripples through results.
That’s the power of this method—a “what-if” tool that tests variables to predict their impact through sensitivity analysis.
At its core, this approach helps answer questions like: “How much would a 10% drop in sales affect profits?” or “What happens if interest rates rise?” By adjusting inputs—like material costs or market trends—you uncover which factors matter most in your analysis.
For example, companies use the mental model to weigh risks in stock investments or bond pricing, illustrating the importance of this method.
Think of it as a stress test for decisions. If you’re choosing between job offers, you might evaluate how the probability of a better opportunity changes your choice.
The higher the “sensitivity index” of a variable, the smaller the tweak needed to sway your decision. This clarity reduces guesswork and builds confidence in the results sensitivity.
Why does this matter? Whether you’re managing a budget or launching a product, understanding key drivers and their values saves time and resources.
Ready to see how this method transforms uncertainty into actionable insights through sensitivity analyses?
Key Takeaways
- The sensitivity analysis mental model dentifies which variables most influence outcomes through sensitivity analysis
- Reduces uncertainty in financial and strategic planning using various methods
- Works through scenario testing (e.g., stock market shifts) in this analysis
- Helps prioritize high-impact factors using sensitivity indexes in the model
- Used by businesses to validate decisions under changing conditions Highlights key results in each section of analysis
Introduction to Sensitivity Analysis
What if you could predict how small changes affect big decisions? This method acts like a financial weather forecast, showing how shifting conditions might alter your results. It’s not magic—it’s about testing variables in a structured model to reveal hidden risks and opportunities.
Definition and Purpose
At its simplest, this approach measures how tweaking one input—like material costs or customer demand—changes your final outcome. Think of a lemonade stand: adjusting prices by 10% could triple profits or empty your pitcher. Businesses use it to spot which factors matter most, whether launching products or pricing bonds.
Why It Matters in Decision-Making
Ever faced a choice where uncertainty kept you stuck? By stress-testing scenarios through sensitivity analysis, this tool turns vague worries into clear action steps.
For example, hospitals use it to prepare for medication shortages, while engineers test bridge designs against extreme weather. The goal? Find your “leverage points”—variables with outsized impact on your results sensitivity.
Three reasons teams rely on it for effective analysis:
- Pinpoints critical variables quickly, enhancing sensitivity
- Reduces guesswork in budget planning by clarifying values
- Builds confidence during market shifts through various methods
Whether you’re managing a startup or a stock portfolio, understanding these dynamics helps you adapt faster to changing distributions. Ready to make unpredictability work for you?
Core Concepts Behind the Mental Model

How do experts predict outcomes when so many factors are in play? The answer lies in understanding two critical pieces: independent variables (the ones you control) and dependent variables (the outcomes you measure).
Think of them as levers and results—pull one lever, watch what happens.
Independent vs. Dependent Variables
Imagine planning a marketing campaign. Your budget (independent) directly affects sales (dependent). If you double ad spending, do sales jump 50% or 200%? This relationship shapes how models forecast real-world results.
Here’s why this matters:
- Independent variables are your inputs—like material costs or interest rates
- Dependent variables show the outputs—profit margins or bond prices
A hospital might test how staffing levels (independent) affect patient recovery rates (dependent). Small tweaks reveal which factors create the biggest ripple effects.
One study found that adjusting medication dosages by just 5% could cut hospital stays by 12 days.
Why does this distinction matter? Without it, you’re guessing which knobs to turn. By mapping these relationships, you build models that turn “what if?” into “here’s what happens.”
Ever changed one ingredient in a recipe and ruined the dish? That’s variables at work—now imagine scaling that to business decisions.
Step-by-Step Guide to Conducting Sensitivity Analysis
Want to make confident decisions even when numbers keep changing? Let’s break down the process into bite-sized steps. Start by building a financial model that mirrors your real-world scenario—like a sales manager forecasting next quarter’s revenue.
Setting Up Your Model
First, list your key inputs: prices, costs, growth rates. Assign realistic values to each. For example, if you sell coffee, input current bean costs ($5/lb) and average daily customers (200). Tools like Excel help organize these numbers into clear data tables.
Always test your model’s logic. Does a 10% price hike lower sales by 5% or 15%? Use formulas like compound annual growth rate (CAGR) to check if results align with historical trends. One bakery found that tweaking flour costs by $0.50 changed profit margins by 8%!
Adjusting Key Variables for Impact
Now, play with the numbers. Increase material costs by 20% or drop customer traffic by 30%. Watch how these shifts affect your outcomes—like net profit or project timelines.
A retail store manager might discover that labor costs impact profits twice as much as rent, emphasizing the importance of understanding cost variables in your case.
Here’s a pro tip: change one variable at a time. If you adjust both marketing spend and product price, you won’t know which drove the result.
In a real-world case, a tech startup learned that delaying their launch by one month reduced annual revenue by 22%—a critical insight for planning and a valuable study in sensitivity analyses.
Finally, document every test. Patterns emerge faster when you track how small tweaks create big ripples.
Using data from your analyses can help simulate different scenarios. Ready to turn uncertainty into your superpower?
Applying Sensitivity Analysis in Decision-Making

Imagine deciding whether to expand your business. You assume sales will grow 10% yearly—but what if they drop? This tool helps managers test these assumptions before committing resources.
A friend once launched a product assuming high demand, only to discover shipping costs erased profits. Testing different scenarios first could’ve saved months of work.
How do changes in data sway choices? If material costs jump 15%, does your project still make sense?
By adjusting inputs like labor hours or interest rates, you spot risks early. One bakery owner found raising cake prices by $2 had little impact—but a $0.50 flour increase cut margins sharply.
Managers use this approach to plan smarter. For example:
- Testing if a 20% traffic drop still justifies opening a new store
- Checking how loan rate changes affect expansion timelines
- Comparing staffing assumptions for holiday sales peaks
Ever wondered which assumptions matter most? Ask: “What breaks this plan?” If shifting one variable flips the result, you’ve found your weak spot. Teams use these insights to build flexible strategies—because real-world decisions rarely follow spreadsheets perfectly.
Real-World Examples of Sensitivity Analysis
What happens when a store suddenly gets busier? Let’s explore how real teams use data-driven tools to answer this. Meet Sarah, a retail manager who boosted sales by studying foot traffic patterns this year.
Case Study: Sales and Customer Traffic Impact

Sarah noticed her store had 1,200 weekly visitors but stagnant sales. Using a simple method, she tested how a 10% traffic increase would affect transactions. Here’s how it worked:
- Tracked current conversion rates (25%)
- Added 120 simulated visitors to her data model
- Calculated new sales projections using historical averages
The result? Extra customers generated 18% more revenue—without changing prices or products. But here’s the twist: when she applied this same approach to holiday seasons, the gain jumped to 31%! This shows why timing matters in analyses.
Teams often overlook three key details:
- Peak vs. off-peak hour conversions differ wildly
- Staffing levels directly affect customer experience
- Weather patterns (like rain) can skew year-over-year comparisons
Sarah’s story isn’t unique. Many managers use this method to spot hidden opportunities. Could your team benefit from similar “what-if” tests? Whether you run a coffee shop or an online store, systematic analyses turn guesswork into strategy.
Sensitivity Analysis in Financial Modeling and NPV
Why do bond prices swing when news breaks about rate hikes? Let’s explore how small shifts in interest rates ripple through financial models—and what that means for your portfolio.
Picture this: a 1% rate increase could slash a bond’s value by 8%, turning a safe bet into a loss. Tools like sensitivity analysis help investors spot these risks before they strike.
Impact of Interest Rates on Bond Prices
Bonds and rates move like seesaws. When rates rise, existing bonds paying lower yields become less attractive. A study of corporate debt showed that a 2% rate jump could erase 15% of a bond’s market value. How much could a tiny rate shift alter your returns? Let’s break it down:
- A 10-year bond priced at $1,000 might drop to $920 if rates climb 1%
- Investors use NPV calculations to compare future cash flows against today’s rates
- Models often test scenarios like “What if inflation stays high for 3 years?”
Here’s where data becomes your compass. By adjusting rate assumptions in spreadsheets, you see how different factors—like loan terms or payment dates—affect profits. One pension fund avoided a $2M loss by testing how delayed rate cuts impacted their bond ladder.
Think of it as financial weatherproofing. If your model crumbles under a 0.5% rate change, it’s time to rebuild. Ready to turn rate risks into strategic advantages?
Strengthening Business Models Through Sensitivity Analysis

What separates thriving businesses from those stuck in survival mode? Often, it’s their ability to test-drive decisions before committing.
Picture a coffee shop owner weighing whether to buy cheaper beans. A quick simulation shows how this cost change affects profits—without risking real money.
This method shines when refining business plans. By tweaking one variable—like shipping fees or ad budgets—you see which cost cuts boost margins versus those that hurt quality.
One bakery found switching flour suppliers saved 12% annually with zero effect on taste. That’s strategic optimization in action.
Here’s how to apply it:
- Build a digital twin of your operations using spreadsheet tools
- Test variables individually (e.g., labor hours vs. material costs)
- Measure the effect of each change on key metrics like ROI
Ever wondered why some companies bounce back faster during recessions? They’ve stress-tested their models through simulations. A 20% rent hike might cripple one retailer but barely dent another who pre-negotiated flexible lease terms.
Start small. Adjust your top three expenses in a virtual sandbox. You’ll quickly spot which tweaks strengthen your foundation—and which ones crack it. Ready to turn financial guesswork into precision planning?
Utilizing Sensitivity Analysis in Healthcare and Nursing Research

Missing patient data doesn’t have to derail your research. Imagine a clinical trial where 15% of participants skip follow-ups.
How do you ensure your conclusions still hold? This is where structured testing shines—helping nurses and researchers navigate gaps while maintaining trust in their findings.
Addressing Missing Data and Outliers
Healthcare teams often face incomplete records. For example, a recent nursing study tested three approaches when 20% of patient pain scores were missing. They found that using median imputation (replacing gaps with typical values) kept results reliable compared to excluding data entirely.
Outliers—like one patient’s extreme recovery time—can skew results in any sensitivity analysis. Researchers might test if removing these data points changes conclusions regarding the overall distribution of outcomes.
One team discovered that excluding two outliers reduced a drug’s perceived effectiveness by 34%, revealing hidden risks in their initial analyses and methods.
Evaluating Research Findings for Robustness
How do you know if a treatment works across diverse groups? By testing scenarios like:
- Does the therapy help seniors as much as younger adults?
- What if clinic locations affect outcomes?
A diabetes study showed medication worked 22% better in urban areas. This uncertainty pushed researchers to adjust their methods and recommendations for rural clinics. The sensitivity analysis revealed the number of patients affected by location variations, highlighting the importance of understanding the level of impact on outcomes.
Simple checks add immense value. Swapping analysis methods or retesting with adjusted variables builds confidence. When one hospital changed how they measured patient mobility, fall risk predictions improved by 18%, showcasing the distribution of results across different sections of the patient population.
Your turn: Could your next study benefit from these stress tests? Even imperfect data can guide better care when approached systematically through sensitivity analyses and simulation methods.
Comparing Sensitivity Analysis and Scenario Analysis
Have you ever faced a decision where both details and big-picture risks mattered? Let’s unpack two tools that tackle these challenges differently.
Sensitivity testing tweaks single variables—like interest rates—to see ripple effects. Scenario planning imagines entire futures, like economic downturns or supply chain disasters.
Think of it like weather prep. Checking how a 10% rain chance affects your picnic is sensitivity work. Planning for thunderstorms, heatwaves, and humidity? That’s scenario territory. One zooms in; the other pans out.
Key differences:
- Focus: Sensitivity isolates variables (e.g., 5% material cost hike). Scenarios bundle factors (recession + labor strikes)
- Use cases: Interest rate shifts suit sensitivity. New market entries need scenario planning
- Output: Sensitivity shows “if X, then Y.” Scenarios reveal “if A+B+C happen, here’s Plan Z”
A real-world example: When interest changes hit bond prices, sensitivity models pinpoint breakpoints. But scenario tools helped one airline survive COVID by simulating travel bans, fuel spikes, and staffing crises together.
Which method fits your next big decision? Use sensitivity for focused “what-ifs” and scenarios when uncertainty runs wild. Both belong in your toolkit—like having both a microscope and a telescope.
Advantages and Limitations of Sensitivity Analysis
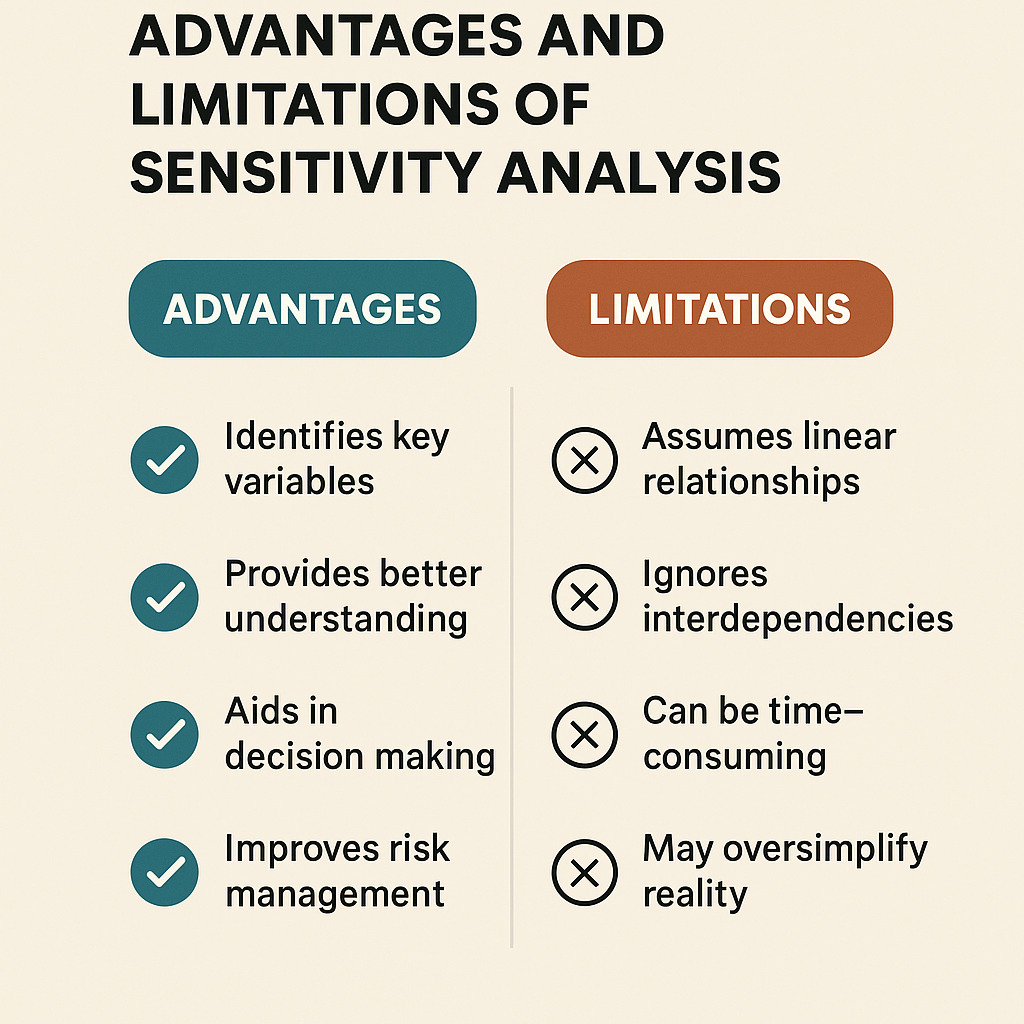
How do you balance confidence and caution when making high-stakes decisions? This method acts like a financial seatbelt—keeping plans secure while revealing hidden bumps. Let’s explore its strengths and pitfalls through real-world scenarios.
Key Benefits for Risk Management
Ever saved a project by spotting a hidden flaw? Teams use this approach to:
- Pinpoint which variables could sink profits (like sudden rent hikes)
- Test backup plans for supply chain delays or price shifts
- Compare how different scenarios affect timelines and budgets
A tech startup avoided disaster by testing how a 3-month coding delay would impact funding. Their model showed a 40% revenue drop—prompting them to hire extra developers upfront.
Identifying Notable Challenges
But what if your assumptions are wrong? This tool has limits:
- Models rely on accurate data—garbage in, garbage out
- Complex systems (like global markets) have too many moving parts
- Results can’t predict exact outcomes—just trends
One hospital learned this the hard way. Their staffing model assumed steady patient flow but collapsed during flu season. The difference between theory and reality? 28% longer wait times.
Use this guide to weigh trade-offs. Test key scenarios, but always pair results with real-world checks. After all, even the best map needs a compass.
Tools and Techniques for Effective Sensitivity Analyses

Picture this: You’re halfway through a project when a supplier suddenly raises prices. Which tools help you quickly measure the impact? Let’s explore practical options that turn raw data into clear action steps.
Start simple with Excel’s data tables. These let you test variables like material costs or interest rates in seconds.
For example, a bakery owner might use them to see how flour price swings affect cookie profits. Pair this with tornado diagrams to visually spot which factors matter most.
Need more power? Try specialized tools:
- Python libraries (NumPy, pandas) automate complex calculations
- R packages like ‘sensitivity’ handle advanced statistical models
- RISK for Excel adds Monte Carlo simulations to spreadsheets
A construction firm recently used these methods to compare concrete suppliers. By adjusting delivery times and costs in their model, they saved 14% on materials without delaying projects.
Three tips for sharper results:
- Always validate your model with real-world data first
- Run one-way tests before combining variables
- Use spider plots to track multiple changes at once
Why does technique choice matter? Picking the right tool can mean the difference between spotting a 5% profit risk and missing it entirely. Ready to make your next decision bulletproof?
Best Practices for Reporting Sensitivity Analysis Results
Ever spent hours crunching numbers only to have colleagues say, “I don’t get it”? Clear reporting turns complex data into decisions people trust. Start by explaining your methods in plain language—like how a retail manager might simplify traffic impact charts for store owners.
Communicating Findings Clearly
Use visuals to show relationships. A color-coded table can highlight which variables sway profits most. For example, mark price changes in red if they drop margins below 10%. Tools like Excel’s conditional formatting make patterns pop without technical jargon.
Three rules for impactful reports:
- Limit results to your top 3-5 drivers—too many numbers overwhelm
- Compare scenarios side-by-side (“If X happens, we gain $Y”)
- Note data limits upfront (“We assumed stable shipping costs”)
Transparency builds credibility. A healthcare team once shared how missing patient data affected their conclusions—and won stakeholder buy-in. Tools like spider plots or tornado diagrams help show sensitivity ranges visually.
Ask yourself: Could a new hire grasp your main points in 90 seconds? If not, simplify. Replace phrases like “multivariate regression” with “tested different combinations.” Your goal? Turn “Huh?” into “Let’s act.”
Integrating Sensitivity Analysis Into Your Analytical Workflow
How often do you check if your decisions hold up when numbers shift? Making this method part of your routine turns guesswork into a repeatable process.
Start by adding quick “what-if” checks to existing tasks—like updating budget forecasts or evaluating project risks using sensitivity analyses.
- Identify your top three variables (e.g., material costs, customer traffic)
- Build a basic Excel model using Data Tables or Goal Seek to analyze cost distributions
- Run weekly tests adjusting one variable at a time to see the effect on outcomes
- Track how outcomes change in reports or dashboards through simulation
A coffee shop owner used this method to handle bean price swings. By linking their POS system to a spreadsheet, they saw how a $0.20 cost increase would impact profits within minutes. This let them adjust menu prices before losses piled up.
Teams using this structured approach report three benefits:
- Faster responses to supply chain hiccups
- Clearer visibility into profit drivers
- Reduced panic during market shifts
Could your next project benefit from these checks? Try adding one variable test to your next planning meeting. Small steps create habits—and habits build resilient strategies.
Sensitivity Analysis Mental Model Tips
Seasoned professionals often spot risks others miss. How? They’ve mastered the art of testing assumptions systematically. Let’s unpack lessons from finance, tech, and healthcare experts who’ve navigated unpredictable markets.
Lessons from Industry Practitioners
A SaaS company reduced capital needs by $2.1M using one trick: rating variables by impact. They focused on product-led growth metrics first—like free trial conversion rates—before testing secondary factors. This prioritization saved months of guesswork.
Three rules experts swear by:
- Update models quarterly—market conditions shift faster than spreadsheets
- Use tools like Oracle Crystal Ball for complex simulations
- Always pair probabilistic thinking with structured tests
Data distribution matters more than you think. One hospital improved staffing forecasts by 19% after adjusting for weekend patient surges. Their secret? Testing how uneven data spreads affect results.
Ever faced a project where small tweaks caused chaos? A retail chain avoided this by stress-testing holiday traffic assumptions. They discovered peak-hour sales contributed 63% of daily revenue—a detail their original model overlooked.
Final tip: Start simple. Rate your top three variables, run quick checks, and expand gradually. As one engineer put it, “Perfection stalls progress. Better rough insights now than flawless answers too late.”
Ensuring Accuracy Through Methodical Approaches
How can you trust your data when so much rides on it? Validating assumptions isn’t just about checking boxes—it’s about stress-testing your logic. Let’s say you’re tracking sales trends but 15% of customer feedback is missing.
Do your conclusions still hold? A healthcare study found that replacing gaps with median values kept results reliable, while ignoring missing data skewed outcomes.
Validating Underlying Assumptions
Start by asking: “What breaks my model?” For example, if excluding one outlier changes profits by 20%, that’s a red flag. A retail team discovered high-spending customers (just 5% of their base) drove 40% of revenue. Removing those data points flipped their entire strategy.
Here’s how to methodically check your work:
- Test variables at different levels—like price hikes of 5%, 10%, and 15%
- Compare results across methods (e.g., complete data vs. estimates)
- Use visual tools like scatter plots to spot hidden patterns
One key point? Always document how each change affects outcomes. When a tech firm adjusted user growth assumptions, they realized a 2% monthly level shift could delay profitability by 18 months. Tools like Bayesian updating help refine assumptions as new data arrives.
Why does this matter? Small tweaks expose big risks. By systematically validating every point, you turn “I think” into “I know.” Ready to make your next decision bulletproof?
Conclusion
Every choice becomes clearer when you see how pieces connect. This mental model gives professionals a structured way to test assumptions—whether pricing products or planning vaccine rollouts. F
rom coffee shops tracking bean costs to hospitals predicting bed needs, the core principle remains: small changes create big ripples. Conducting a sensitivity analysis can reveal how different factors impact the overall outcome.
Think like an analyst, not a fortune-teller. Build models that answer “What breaks this plan?” then adjust. Engineers use it to reinforce bridges; marketers optimize ad budgets.
The method works because it turns abstract worries into measurable scenarios, often through sensitivity analyses that assess various distributions of input values.
Your next move? Start simple. Track three key factors in your work—maybe project timelines, material costs, or customer retention. Test one change at a time using free tools like Excel. Y
ou’ll quickly spot which tweaks matter most, and how each case impacts the overall cost and outcome.
True power lies in consistent practice. Update your models quarterly. Share findings visually with spider charts. Over time, you’ll make decisions faster and explain them better.
That’s the mark of a skilled analyst—turning uncertainty into your strategic advantage, one systematic check at a time.


