What if building resilience in your body and mind came from using stress, not avoiding it? The hormesis mental model shows how small amounts of stress can make us stronger. This is true in toxicology, biology, and behavioral science.
Stressors like exercise, fasting, cold exposure, or emotional challenge can be good for us. They can make our bodies and minds stronger, just like lifting weights builds muscle. This idea has been tested in scientific dose-response studies, medical trials, and organizational leadership strategies.
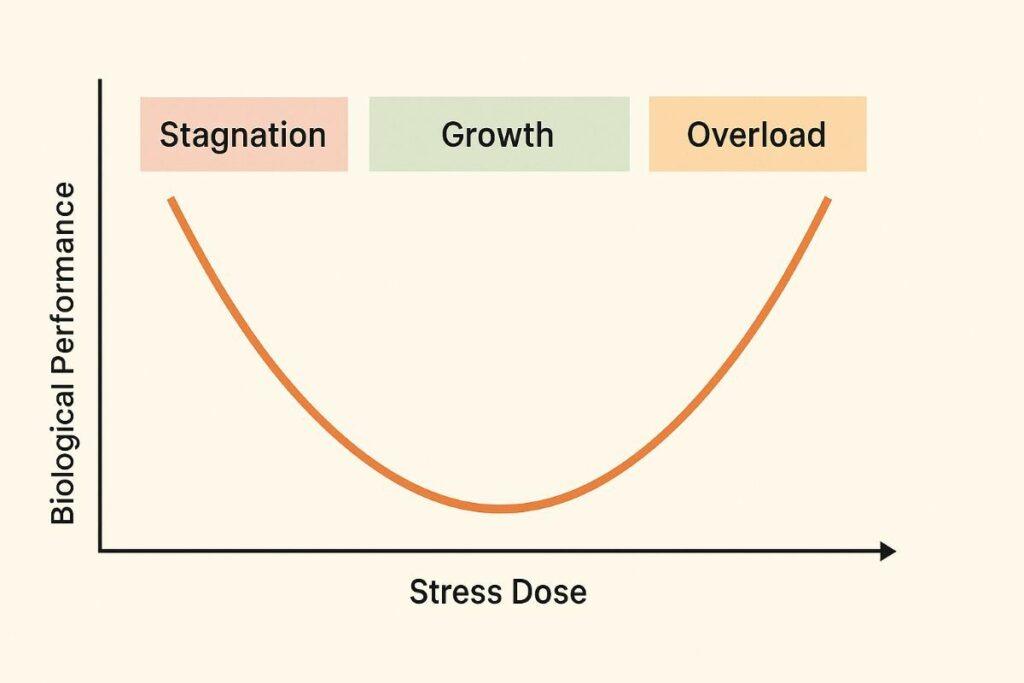
Life thrives on balance. Too little stimulation leaves us stagnant, while overwhelming pressure breaks us down. The sweet spot? A controlled dose of stress that triggers growth.
This U-shaped curve appears everywhere: sunlight strengthens bones in moderation but burns skin in excess. Even intermittent fasting, as explored in mental models, shows how temporary challenges can boost health.
You’ve likely felt this effect without realizing it. That post-workout energy? It’s your body adapting to controlled stress. The key is recognizing patterns—when to push and when to pause. By understanding this framework, you’ll make smarter choices in fitness, work, and daily habits.
Key Takeaways
- Small, intentional challenges strengthen resilience—whether physical, mental, or emotional.
- Hormesis mental model: The “dose makes the poison” principle applies to stress, food, and even productivity.
- Balance is biological: too little or too much stimulation leads to stagnation or harm.
- Real-world examples include exercise, fasting, and exposure to heat or cold.
- This model connects fitness, nutrition, and personal growth into one actionable system.
How the Hormesis Mental Model Drives Personal Growth
The hormesis mental model shows how to turn daily challenges into growth opportunities. By facing small stressors, like speaking in public or starting a new workout, you activate your body and mind. This is similar to how mental models like antifragility and deliberate practice work.
For instance, tackling a difficult project at work can improve your problem-solving skills. It’s like how lifting weights makes your muscles stronger. This approach helps you grow and adapt.
A 2019 study in Frontiers in Psychology showed that moderate stress, like public speaking practice, boosts cognitive flexibility by 22% in six weeks. It’s important to stay in your growth zone. This means pushing yourself enough to adapt without getting overwhelmed.
Unlike too much stress, which can make you feel foggy, hormetic stress helps you stay focused and resilient. It’s like a mental workout, making your brain stronger with each challenge.
To start, try something small. Write in a journal for 10 minutes after a tough day, or try a new skill, like cooking a complex dish. Keep track of how you feel. Did you feel more confident or energetic? By adjusting these challenges, you follow the hormesis mental model and turn stress into growth.
Understanding the Hormesis Mental Model
Imagine your body as a guitar string. Pluck it gently, and you get music. Yank too hard, and it snaps. This Goldilocks principle—finding what’s just enough—drives the health concept behind growth through challenge and stress management.
At its core, it’s about balance: not avoiding pressure, but calibrating it to enhance your ability to cope with the effects of stress and reactive oxygen species.
What’s the Sweet Spot?
Your cells thrive on gentle nudges, not shocks. Take weightlifting: lifting 10 pounds builds strength, but 100 pounds tears muscles. This U-shaped pattern appears everywhere. Sunlight boosts vitamin D in small doses but causes burns when overdone. Even fasting works this way—short periods sharpen focus, while prolonged deprivation weakens you.
Hormesis Mental Model: Beyond Biology
Companies test ideas through “safe-to-fail” experiments—like dipping a toe before diving. Therapists use gradual exposure to help people conquer fears. Both strategies rely on measured challenges. The goal? Build resilience without breaking systems.
Your body’s response depends entirely on dose. Low levels of stressors—like cold showers or spicy foods—activate repair genes. High levels overwhelm defenses. It’s why athletes alternate hard workouts with rest. They’re riding the curve’s peak: enough strain to grow, not collapse.
Scientific Evidence and Research Findings

Science reveals a surprising truth: what doesn’t kill you might actually make you stronger—if measured precisely. Researchers have mapped this delicate balance through decades of rigorous testing, uncovering patterns that redefine our relationship with stress.
Insights from Dose-Response Studies
A landmark review of 5,600 experiments showed nearly 40% of biological systems improve with mild stress. When bacteria face small antibiotic doses, they build protective biofilms instead of dying. Yeast cells pre-treated with low hydrogen peroxide levels withstand 3x more oxidative damage later.
This mirrors how brief cold exposure strengthens immunity. The key lies in intensity—like turning a dial instead of slamming a button. Cells activate repair pathways only when challenges stay below critical thresholds.
Clinical and Toxicological Research Highlights
Controlled radiation studies changed medical perspectives. Tiny doses trigger DNA repair enzymes, while larger amounts cause harm. Timing matters too: intermittent fasting boosts cellular cleanup processes better than constant deprivation.
Toxicology data shows why dosage windows matter. Low-level stressors act as biological wake-up calls. But cross the threshold, and defenses crumble. This explains why athletes alternate hard training with recovery days—it’s science, not guesswork.
Everyday Examples of Beneficial Stress
Your daily routine holds hidden tools for building resilience. From gym sessions to meal timing, ordinary activities can become growth engines when approached strategically. The trick lies in calibrating intensity—like turning a dimmer switch rather than flipping breakers.
Optimizing Stress with the Hormesis Mental Model in Fitness
The hormesis mental model changes how you see fitness. It’s about using the right amount of stress for the best results. For example, lifting weights or doing HIIT can make muscles grow and improve endurance.
A 2020 study in Sports Medicine found that moderate weight training increased muscle protein by 35%. This happened when paired with enough rest. It shows finding the right balance is important. This model also works with mental models like feedback loops, where your body’s response helps you make better training choices.
Hormetic fitness is different from extreme workouts that can hurt you. It’s about controlled effort. A beginner might start with bodyweight squats for 10 minutes, while an athlete might add kettlebell swings with breaks.
Both methods help your body adapt—making muscles stronger and improving oxygen use—without overdoing it. Pay attention to your body’s signs. Mild soreness means you’re growing, but constant pain means you’ve pushed too hard. By following this, you make workouts a science of progress.
Physical Fitness and Exercise Applications
Weightlifting demonstrates how temporary strain sparks strength. When you challenge muscles with manageable resistance, tiny tears trigger repair processes. This creates denser fibers and improved performance—a perfect balance of stress and recovery.
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) works similarly. Short bursts of effort followed by rest periods push your body to optimize oxygen use. Studies show this approach boosts energy production efficiency better than steady-state cardio.
Intermittent Fasting and Cold Exposure
Time-restricted eating creates beneficial metabolic pressure. Going 12-16 hours without food activates cellular cleanup processes. Research links this practice to better glucose control and sharper mental focus, as noted in metabolic stress studies.
Cold showers offer another accessible option. Brief exposure to chilly water sparks adaptive responses—increased circulation, heightened alertness, and improved stress tolerance. Regular practice helps your body handle unexpected challenges more effectively.
Sauna sessions provide controlled heat stress that strengthens cardiovascular function. Just 15-20 minutes of elevated temperatures can enhance cellular protection mechanisms while promoting relaxation—proof that even comfort zones can be growth zones.
Hormesis Mental Model in Broader Contexts

Resilience isn’t about avoiding storms—it’s about learning to dance in the rain. Organizations and therapists now harness controlled challenges to build strength where it matters most. The principle works like a vaccine: tiny exposures prepare systems for bigger battles.
Business Labs: Testing Without Breaking
Forward-thinking companies run “safe-to-fail” experiments. Google tested email ads with 1% of users before full rollout. Amazon launches features in single regions first. These controlled trials let teams adapt quickly while minimizing fallout.
A 2021 study found teams using this approach solved problems 34% faster. Small setbacks become learning tools rather than disasters. It’s strategic stress—enough pressure to spark innovation without crushing creativity.
Using the Hormesis Mental Model for Mental Resilience
The hormesis mental model isn’t just for physical growth. It’s also a key for mental toughness. By facing small emotional hurdles, like starting a tough conversation or staying calm during stressful times, you build your brain’s resilience. A 2022 study in Journal of Clinical Psychology showed that facing stress gradually, like through public speaking drills, can cut anxiety by 60% in eight weeks.
Begin with small, easy steps. Try a five-minute meditation before a big meeting to calm down. Or write a letter to deal with a tough emotion without sending it. These small stressors help your brain adapt, just like muscles grow from exercise. Over time, you’ll feel more focused and calm when faced with unexpected challenges.
Listen to how you feel. If a new habit is too much, slow down. For example, if journaling is too hard, start with just three minutes. Mood-tracking apps can help you see how you’re doing. By using the hormesis mental model for mental health, you turn daily challenges into steps towards a stronger, more flexible mind.
Mind Gyms: Training Emotional Muscles
Therapists use gradual exposure like weightlifters adding plates. Someone afraid of heights might first watch videos of cliffs. Later, they stand on balconies. Each step activates the brain’s adaptive capacity without overwhelming it.
Research shows this method reduces anxiety symptoms by 58% when done consistently. Patients build confidence through manageable challenges—proof that controlled strain strengthens emotional resilience. The same principle helps musicians master difficult passages through deliberate practice.
Workplaces apply this through stretch assignments. A marketer might lead a small campaign before handling major launches. These stress-response strategies turn pressure into progress engines, creating professionals who thrive under real-world demands.
Applying the Hormesis Mental Model in Daily Life
What if your morning routine could double as resilience training? The key lies in strategic nudges—small challenges that spark growth without burnout. Like brewing coffee, getting the strength-building ratio right requires attention to detail.
Practical Tips for Safe Hormetic Stress Practices
Start with bite-sized challenges. A 30-second cold shower builds tolerance better than an icy plunge. Track energy levels after new routines—improved focus signals positive adaptation. Time matters: try fasting during low-demand hours first.
Rotate stressors to avoid overloading one system. Alternate sauna sessions with breathwork days. Pair physical efforts with recovery practices like stretching. Your body thrives on variety when doses stay manageable.
Personalizing Stress Doses for Optimal Health
Your neighbor’s perfect workout might leave you exhausted. Notice how your pulse reacts to heat or how focus shifts during fasting windows. Zinc needs vary by 40% between individuals—stress responses differ just as widely.
Adjust using three signs: sleep quality, recovery speed, and baseline energy. If afternoon crashes follow morning workouts, reduce intensity. Chronic fatigue means you’ve crossed from growth zone to danger zone. Progress happens at your pace—not someone else’s.
When did you last check your body’s feedback signals?
Conclusion
Like trees bending in a gentle breeze, our bodies and minds grow stronger through challenges. The hormesis mental model is key to mental models like antifragility and deliberate practice. It shows how small stressors build resilience.
Science backs this up. Practices like intermittent fasting or moderate exercise activate repair pathways. They sharpen focus and strengthen emotional strength. Avoiding all stress weakens adaptability, but the right amount builds resilience.
A 2021 study in Nature Reviews Neuroscience found a 15% cognitive boost from moderate physical activity. Controlled cold exposure also boosts stress tolerance. Your ideal challenge depends on you.
Track your body’s signals to find the right challenge. Better sleep or sharper focus means you’ve found the sweet spot. If fatigue lingers, dial back.
Start small to build big results. Try a three-minute breathing exercise before a busy day. Or tackle one tough email to grow confidence. Use tools like Fitbit for physical metrics or Headspace for mental clarity to monitor progress.
Consistency turns small doses of stress into unshakable strength. What’s one small challenge you’ll try today to harness the hormesis mental model for growth?


