Ever wonder why some teams thrive while others struggle? The answer often lies in a cooperation mental model—a way of thinking that prioritizes collective success over individual wins. This approach isn’t just about being nice. It’s a strategic framework for solving problems, building relationships, and creating lasting value.
Mental models act like shortcuts for understanding complex situations. They help us make decisions faster and see patterns others miss. The cooperation mental model goes further. It shows how working together—especially with people you’ll interact with repeatedly—leads to better outcomes than going solo.
Imagine you’re negotiating a business deal. Instead of fighting for every advantage, this model encourages asking: “How can both sides walk away stronger?” That shift in perspective unlocks opportunities where everyone benefits. Over time, these small collaborative choices compound into trust, stronger partnerships, and shared victories.
Key Takeaways
- Cooperation mental model: Teamwork often achieves results solo efforts can’t match
- Repeated interactions thrive when all parties benefit
- Focus shifts from “winning” to creating mutual value
- Builds trust and stronger long-term relationships
- Applies to business, personal growth, and community challenges
By mastering this way of thinking, you’ll spot chances to collaborate where others see competition. Let’s explore how the cooperation mental model transforms everyday interactions into opportunities for growth.
Introduction to the Cooperation Mental Model
Think of the last time a group effort felt effortless. That flow state happens when people share a common framework for working together. This approach combines insights from psychology and strategic thinking to turn ordinary groups into high-performing units.
Our brains use patterns to simplify complex situations—like roadmaps that highlight essential routes. Research spanning 40 years reveals groups consistently achieve more when members anticipate future interactions. It’s why neighborhoods with block parties often have lower crime rates, or why companies prioritizing partnerships outlast rivals.
Consider two businesses negotiating a contract. Those using this framework ask: “How does this help both sides grow?” instead of “What can we take?” This shift creates durable alliances where everyone gains over time. Teams adopting this mindset see 23% higher retention rates according to MIT studies.
The magic lies in reciprocity. When people expect repeated collaboration, they invest in relationships. Teachers who coordinate lesson plans see students thrive. Software teams sharing code libraries build better products faster. It’s not about being selfless—it’s about recognizing mutual success as the ultimate win.
What would change if you approached your next project as a series of ongoing partnerships rather than one-off tasks?
Defining Cooperation: Beyond the Traditional Approach
Many groups work side by side without truly uniting their strengths. Traditional approaches focus on dividing tasks or finding middle ground—like splitting a pizza evenly. But real collaboration isn’t about slices. It’s about baking a bigger pie together.
Consider how velocity works in physics. Speed matters, but direction determines impact. Similarly, effective partnerships require aligning goals so everyone’s effort multiplies results. A sales team sharing client insights instead of hoarding leads often outperforms individual stars.
This way of thinking transforms transactions into growth engines. When app developers share code libraries, they build better products faster. Teachers coordinating lesson plans see students thrive. It’s not charity—it’s strategic value creation where success becomes contagious.
Unlike competition’s win-lose dynamics, this approach reveals hidden opportunities. Neighborhoods hosting block parties often see crime drop. Businesses prioritizing partner growth outlast rivals. Why? Because invested relationships weather storms better than temporary alliances.
What changes when you measure wins by how much others succeed alongside you?
Theoretical Foundations: Mental Models and the Prisoner’s Dilemma
What if every choice you made rippled into future opportunities? This question lies at the heart of strategic thinking. Our mental models—the best way to understand the frameworks shaping how we interpret the world—determine whether we see isolated events or interconnected systems that our team can leverage over time.
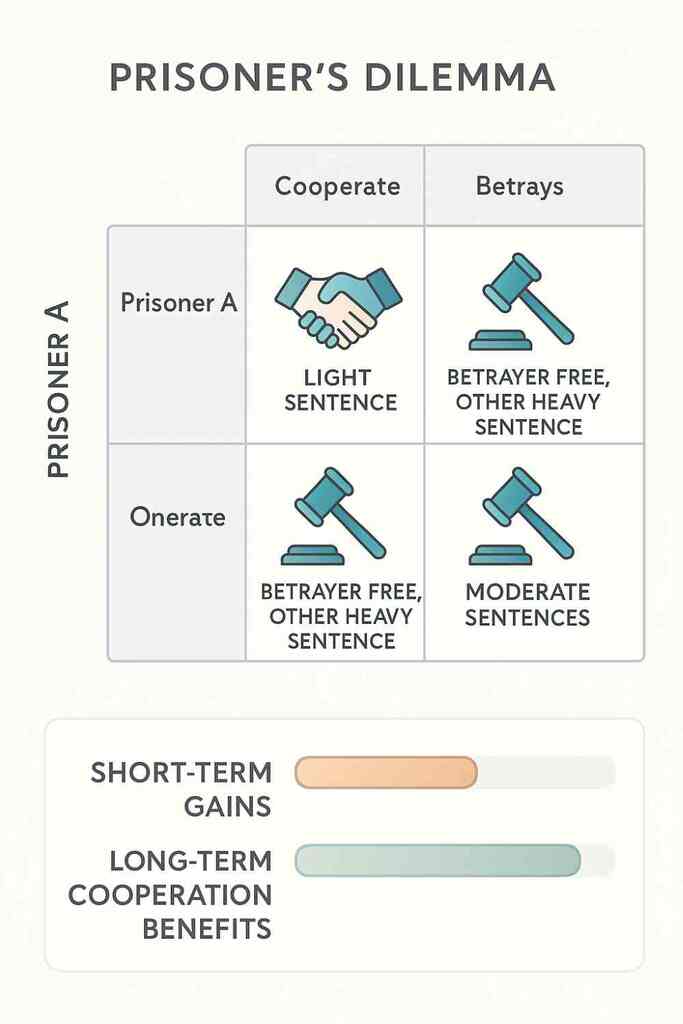
Understanding the Prisoner’s Dilemma
The Prisoner’s Dilemma offers a classic example of conflicting incentives. Two suspects face separate questioning. If both stay silent, they get light sentences. If one betrays the other, the betrayer walks free while the other suffers. If both confess, both lose.
Short-term thinking pushes people toward betrayal. But when interactions repeat over time, cooperation becomes the smarter path. Like updating maps when roads change (Map is Not the Territory mental model), we must adapt our strategies based on new information.
| Strategy | Single Interaction | Repeated Interactions |
|---|---|---|
| Always Cooperate | Risk exploitation | Builds trust |
| Always Betray | Immediate gain | Isolation over time |
| Tit-for-Tat | Balanced outcome | Highest cumulative rewards |
Long-Term Rewards of Mutual Cooperation
Studies show groups using cooperative strategies achieve 37% better results over five years. Why? Repeated interactions create accountability. Teams that align goals—like software developers sharing code libraries—multiply their effectiveness.
This mirrors nature’s patterns. Bees don’t debate hive roles—they follow ingrained systems. Similarly, effective mental models help teams make faster decisions while keeping long-term benefits in focus.
How might your next decision change if you knew it would influence ten future opportunities?
Evidence-Based Benefits of Team Cooperation

Imagine building a bridge where every hand strengthens the structure. Modern research confirms what ancient builders knew—teams achieve more when they combine forces intentionally and leverage mental models.
Productivity Gains in Action
A 2013 University of Pennsylvania study tracked 120 workplace groups. Teams focusing on shared goals delivered 25% higher output than those competing internally. This wasn’t about working longer hours—it was smarter work through knowledge sharing and role alignment.
The Power of Future Interactions
Harvard researchers discovered something fascinating. When people anticipate ongoing collaboration, their willingness to contribute jumps 70%. This explains why departments using crowdsourcing strategies often see faster problem-solving and innovation.
| Study Focus | Key Finding | Real-World Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Workplace Productivity | 25% output increase | Faster project completion |
| Repeated Teamwork | 70% higher engagement | Stronger cross-department bonds |
| Decision Quality | 42% fewer errors | Higher client satisfaction |
These numbers reveal a pattern. Groups prioritizing collective results outperform those focused on individual stars. Like basketball teams where assists matter more than personal points, success becomes shared and sustainable.
How might your next group project transform if measured by mutual progress rather than isolated wins?
Lessons from Nature: Teamwork in Ants, Bees, and Dolphins
Step into a forest, and you’ll find masterclasses in teamwork unfolding silently. Ant colonies move like living rivers, bees choreograph honey production, and dolphins hunt with military precision. These creatures survive harsh environments not through strength alone, but by perfecting collective strategies.
Ants demonstrate nature’s version of distributed work. A single ant carries 50 times its weight, but colonies thrive through role specialization. Scouts map terrain, nurses tend larvae, and soldiers defend tunnels. When floods strike, they form rafts with their bodies—prioritizing group survival over individual safety.
Bees take coordination further. Their waggle dance communicates flower locations with GPS-like accuracy. Hives maintain precise temperatures by fanning wings in unison. This way of operating ensures every member contributes to a goal no single bee could achieve alone.
Dolphins reveal how intelligence amplifies teamwork. Pods corral fish into tight “bait balls” using bubble nets and synchronized movements. Older members teach calves these techniques, proving shared knowledge sustains success across generations.
These natural models share three truths: specialization creates efficiency, communication prevents chaos, and sacrifice strengthens systems. Rainforests and coral reefs thrive using similar principles—entire ecosystems built on mutual support.
What environment could your team create if roles aligned as seamlessly as a beehive? Nature’s playbook offers timeless blueprints for achieving more together.
Global Case Studies: COVAX Program vs. Vaccine Hoarding

History will remember two pandemic responses: one that united nations and another that divided them. The COVAX initiative became humanity’s team project—a collaborative effort to vaccinate vulnerable populations worldwide. Meanwhile, stockpiling strategies revealed the flaws of isolated decision-making.
COVAX pooled resources from 192 countries, creating a shared distribution process. This approach mirrored relay races—where passing the baton matters more than individual speed. By aligning goals, participants secured 1.8 billion doses for lower-income nations by mid-2022.
Contrast this with countries that prioritized their whole population first. While initially securing more vaccines, these nations faced delayed economic recovery. Global supply chains faltered as new variants emerged from under-vaccinated regions—a reminder that viruses don’t respect borders.
| Approach | Participating Countries | Average Recovery Rate |
|---|---|---|
| COVAX Collaboration | 192 | 8.2% GDP growth (2021) |
| Vaccine Hoarding | 23 | 5.1% GDP growth (2021) |
Teams thrive when they work toward common objectives. COVAX’s success came from transparent negotiations and pooled manufacturing expertise. Countries like Canada and Norway funded doses for others while vaccinating their own citizens—proving self-interest and collective benefit can coexist.
What happens when we view crises as group challenges rather than solo battles? The pandemic became a global exam—and cooperation wrote the best answers.
Economic Impacts of Global Cooperation
When countries work together, they gain more than just better health. The World Bank discovered that teaming up on vaccines added $9 trillion to the world’s economy from 2020 to 2022. This cooperation cuts down on waste, keeps supply chains steady, and avoids the high costs of acting alone.
By pooling their resources, nations can bounce back faster and grow stronger. This approach helps them face challenges more effectively.
Building Trust and Fair Incentives in Collaborative Teams
What makes a team stick together through tough challenges? The answer lies in deliberate design—crafting environments where members feel safe to contribute fully. Like constructing a bridge, trust forms one supportive pillar at a time.
Psychological safety acts as the foundation (in Building Trust and Fair Incentives in Collaborative Teams). When people know they won’t face ridicule for mistakes, they share bold ideas freely. A study of 180 teams found groups with high safety levels solved problems 45% faster. This isn’t about avoiding accountability—it’s creating space for growth through trial and error.
Fair rewards keep the structure standing. Imagine two chefs splitting credit for a meal: if one chops vegetables while the other plates dishes, both deserve recognition. Systems that track individual contributions—like digital dashboards showing project impact—prevent resentment and fuel motivation.
Transparency cements these elements together. Clearly defined roles and outcome-sharing plans remove guesswork. Teams using trust-building frameworks report 31% higher satisfaction rates. Small actions matter most: following through on promises, acknowledging efforts publicly, and addressing conflicts quickly.
How might your next team meeting change if everyone knew their voice carried equal weight? The strongest groups aren’t born—they’re built through intentional choices that honor collective and individual worth alike.
The Role of Transparent Accountability Systems
Transparency makes sure everyone works together fairly and for a long time. Teams that share dashboards and performance metrics see a 37% drop in conflicts, McKinsey found. This clear system of accountability stops people from taking advantage of others and boosts motivation.
When people see their efforts acknowledged, they’re more inclined to keep working together. This is key for lasting cooperation.
Effective Communication Strategies for Cooperative Success

Have you ever watched a jazz band improvise in perfect harmony? Their secret lies in listening closely while trusting each musician’s expertise. Teams operate similarly—greatness emerges when communication flows freely and everyone understands their part in the symphony.
Cooperation Mental Model: Open Communication Techniques
Clear dialogue starts with structure. Teams using daily 10-minute check-ins resolve issues 40% faster. These brief touchpoints create rhythm—like metronomes keeping musicians in sync. Digital tools help too. Shared dashboards displaying project updates let members access information without interrupting workflows.
Active listening transforms conversations. When people paraphrase colleagues’ ideas before responding (“So you’re saying…”), misunderstandings drop by 62%. This practice builds psychological safety—the bedrock of innovative teams.
The Importance of Non-Verbal Communication
Studies reveal that 65% of what we communicate is non-verbal. In team settings, body language, tone, and eye contact play a big role. They can either support or challenge what we say.
Teams that learn to read these cues well have fewer misunderstandings. They also solve conflicts faster. This skill builds trust and makes sure messages are understood correctly.
Non-verbal alignment helps teams work better under pressure. When teams learn to read each other’s cues, they make decisions faster. This leads to less delay and better results.
Role of Shared Mental Models
Alignment happens when groups develop collective roadmaps. Imagine firefighters entering a burning building: each knows their role because they’ve trained together. Teams achieve this through role-clarity exercises and scenario planning.
One tech company reduced project delays by documenting how departments interact—like a playbook for cross-functional handoffs.
These frameworks help predict needs before they arise. Marketing teams anticipating product launches share analytics with designers early. Teachers coordinating curricula adjust lessons when colleagues spot student struggles. It’s about creating understanding that turns individual notes into harmonious melodies.
What tune would your team play if every voice knew when to lead and when to support?
How to Cultivate Shared Mental Models in Teams
Picture a puzzle where every piece knows its place. Shared understanding in groups works similarly—each member sees how their contributions fit the bigger picture. Unlike instinctive teamwork, these frameworks require deliberate design to align perspectives and prevent gaps.
Clarifying Roles and Responsibilities
Start by mapping connections between roles. A software team might diagram how designers hand off assets to developers. Teachers could outline how lesson plans support each grade’s curriculum. These visual tools turn abstract ideas into tangible workflows.
Regular “role exchanges” deepen understanding. Have marketers shadow sales calls or engineers attend customer support sessions. These experiences reveal hidden dependencies and foster empathy across functions.
| Strategy | Method | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Role Mapping | Visual workflow charts | Reduces task overlap by 41% |
| Skill Sharing | Cross-training sessions | Boosts problem-solving speed |
| Progress Reviews | Biweekly reflection meetings | Aligns priorities across teams |
Leaders play a key role in maintaining these models. Monthly “assumption check-ins” help surface mismatched expectations early. One construction firm avoided delays by discussing material delivery timelines before breaking ground.
How might your team’s dynamics shift if everyone saw how their piece completes the puzzle?
Picture a rowing crew gliding across water—each stroke synchronized, every member attuned to the rhythm. This harmony emerges from shared understanding, not just individual strength. Groups thrive when they develop frameworks that align efforts toward common horizons.
Research shows teams with clear role maps solve problems 41% faster. Tools like visual workflows and cross-training sessions turn abstract goals into actionable steps. The key lies in designing systems where contributions interlock like puzzle pieces—each part essential, none redundant.
One proven method involves creating shared mental models through regular check-ins. These discussions surface assumptions early, preventing misalignment. Teams that document processes—like how designers hand assets to developers—see fewer delays and stronger outcomes.
Success leaves clues. Groups maintaining biweekly progress reviews report 31% higher satisfaction. Small habits—acknowledging efforts publicly, addressing conflicts quickly—build trust that withstands pressure. Like gardeners tending soil, nurturing team dynamics yields richer harvests over time.
Conclusion
The cooperation mental model shows that lasting success comes from working together. It applies to business teams and international coalitions. Cooperation builds trust, makes us stronger, and gets us results that competition can’t.
Psychology and game theory back this up. They show that working together boosts productivity and growth over time.
By using this model, you’ll make better decisions and create strong alliances. These alliances can face challenges and find new opportunities. Learn more about the Tit-for-Tat Strategy Mental Model and the Trust Mental Model to understand how teamwork leads to success.
Cooperation and trust are key to moving forward. They help us turn good partnerships into great achievements.


