In today’s digital world, over 330 million tweets are sent out every day. The Brandolini Law mental model, also known as the Bullshit Asymmetry Principle, explains why lies spread faster than truths. It takes a lot more effort to debunk a false claim than to share it.
This model helps us understand why false information can spread so quickly. It’s not just about social media. It’s also about gossip in the office or rumors on X (formerly Twitter). Learning about this can help you save time and keep your mind clear.
First described in 2013 by Italian developer Alberto Brandolini, this principle states that “bullshit takes 10x more energy to correct than to create.” One careless tweet can ignite global confusion, while fact-checkers scramble to contain the damage. The imbalance shapes everything from social media debates to workplace rumors.
Why does this matter today? False claims now travel faster than ever. A viral conspiracy theory might reach millions before breakfast. Meanwhile, detailed corrections often gather dust in academic journals.
Understanding this asymmetry, often referred to as the Brandolini Law, helps you decide when to engage—and when to conserve your energy to refute bullshit effectively.
Through this article, you’ll discover:
Key Takeaways
- The Brandolini Law mental model shows how a single tweet becomes a vital tool for navigating modern information wars
- Why false claims spread faster than corrections in social networks
- Real examples showing how misinformation impacts daily decisions
- Practical strategies to identify content worth your attention
- Methods to protect your time from endless “bullshit” cleanup
By mastering the Brandolini Law mental model, you’ll learn to cut through digital noise without drowning in it. Let’s explore how to thrive in a world where truth demands patience—and discernment.
How the Brandolini Law Shapes Online and Offline Behavior

The Brandolini Law isn’t just about social media. It impacts workplaces, schools, and family talks too. A single wrong comment in a meeting can ruin a project. Just like how one viral post can confuse millions.
Research shows online lies spread faster than true news. In workplaces, rumors can cut productivity by 40% in a day. Knowing this helps us choose what to challenge and what to ignore.
This law helps us decide what’s worth our time. We should focus on what’s important and ignore the rest.
Introduction to Brandolini’s Law

Imagine spending three minutes crafting a social media post—and three hours defending it against people who refute bullshit. This imbalance lies at the heart of what’s now recognized as a critical pattern in modern communication.
The bullshit asymmetry principle reveals why quick claims often overpower careful corrections, despite the evidence and examples available to support accurate information.
Overview of the Concept
The asymmetry principle emerged from real-world political clashes. Observers noticed how easily misleading statements could dominate debates, while factual rebuttals struggled for attention.
Inspired by Daniel Kahneman’s research on decision-making, this idea gained traction through practical examples—like watching media figures weaponize half-truths, highlighting the amount of energy needed to refute bullshit order magnitude claims.
Relevance in Today’s Information Landscape
A 2018 MIT study showed false claims spread six times faster than truths on Twitter. Social platforms reward speed over accuracy—tap “share” before checking sources.
This creates what Italian blogger Uriel Fanelli called a “shit mountain”: endless misinformation outpacing cleanup efforts, with an order magnitude of falsehoods that is order magnitude bigger than the truth.
Digital tools amplify the problem. One viral meme can sway opinions globally, while detailed fact-checks reach limited audiences.
Recognizing this amount of energy needed to counter misinformation is crucial, as the asserted without evidence claims often overshadow factual corrections.
Understanding this order of information flow helps you prioritize what deserves your energy—and what’s better left unchallenged.
Understanding the Asymmetry of Misinformation

Why does a five-second lie take fifty minutes to unravel? This imbalance defines our modern information battles. False claims multiply like weeds—effortless to plant, exhausting to uproot. The bullshit asymmetry principle explains why quick fiction beats slow facts every time.
Energy to Refute vs. Energy to Spread
Creating confusion requires minimal effort: a catchy phrase, an emotional trigger. Correcting it demands research, logic, and patience. Imagine building a house of cards versus reconstructing a collapsed building.
One takes seconds. The other needs blueprints, illustrating the burden proof needed to dismantle falsehoods. This work is often dismissed as bullshit, yet it’s essential for clarity.
Misinformation thrives on vagueness. A claim like “They’re hiding the truth!” needs no proof. Debunkers must define “they,” identify the “truth,” and disprove the hiding—a three-act play most audiences skip.
For example, they must present evidence to counter these claims, turning the order of arguments on its head.
Brandolini Law Mental Model Psychological and Social Factors
Our brains prefer shortcuts. Simple lies fit neatly into existing biases. Complex truths? They demand mental gymnastics. Studies show people share content that feels true 6x faster than verified facts—even when they know better.
Social dynamics amplify this. Admitting error feels like losing status. Defending false beliefs becomes tribal loyalty. That’s why corrections often backfire—proof meets pride, and pride digs in deeper.
Recognizing this asymmetry helps you choose battles wisely. Not every myth needs slaying. Focus on claims with real consequences, and let the rest fade un-fed.
Psychological Traps That Fuel the Spread of Bullshit
Our minds are wired for speed, not depth. That’s why catchy lies spread quickly, while true stories struggle to get noticed. Studies from MIT and Stanford show that false headlines grab more attention than real ones.
This isn’t just a web issue. At work, rumors spread because they match our fears or past experiences. When everyone seems to agree, these false claims grow even faster.
Knowing this helps you avoid spreading misinformation. It also teaches you when it’s best to stay quiet.
Origins and History of The Brandolini Law Mental Model

A single tweet changed how we understand information wars. In January 2013, an Italian programmer watching political debates typed 23 words that became a powerful source of armor against digital chaos, illustrating the brandolini law.
This idea resonated with many people, highlighting the effort required to sift through misinformation and the things we accept as truth.
From Alberto Brandolini’s Tweet to a Global Adage
Alberto Brandolini saw systems everywhere. As a software developer, he noticed patterns—like how bug fixes took ten times longer than creating errors. Then came Silvio Berlusconi’s media battles. Political claims flew fast; fact-checkers drowned in rebuttals.
Daniel Kahneman’s work on thinking modes crystallized it. “Fast” thinking loved catchy lies. “Slow” thinking demanded proof. Brandolini’s tweet comparing bullshit cleanup to energy ratios went viral—not because it was new, but because it fit our times perfectly.
2013 marked social media’s teenage years. Platforms rewarded speed, not truth. His observation became a shield for teachers, journalists, and anyone drowning in online falsehoods.
Ancient philosophers had hinted at truth’s fragility, but this was different—a math equation for modern madness.
Today, the principle explains vaccine myths and office gossip alike. It started with one person connecting coding logic to human behavior.
Sometimes, the best solutions come from unexpected places—like a programmer reading psychology during Italy’s political storms.
The Bullshit Asymmetry Principle Explained

Some phrases sound wise but crumble under scrutiny. Philosopher Harry Frankfurt called this phenomenon “bullshit”—not lies, but statements made without regard for truth. Unlike deliberate falsehoods, bullshit floats in a gray area where accuracy doesn’t matter—only impact.
Defining Bullshit and Its Characteristics
Bullshitters aim to persuade, not inform. Imagine someone claiming “quantum energy aligns your chakras.” It’s vague enough to sound scientific yet impossible to disprove. This pseudo-profound bullshit uses complex terms to hide emptiness—like wrapping air in glitter paper.
Three traits expose bullshit: 1. Mushy language (“Some people say…”) 2. Buzzwords without context (“synergy,” “disruptive innovation”) 3. Emotional triggers over evidence (“They don’t want you to know!”)
Frankfurt noted bullshitters often accidentally tell truths. A broken clock is right twice daily—but still broken. This makes bullshit dangerous. It’s not just wrong; it’s indifferent to rightness.
Why does this asymmetry principle matter? Spotting bullshit early saves energy. When a colleague claims “data suggests” without showing numbers, or a post declares “everyone’s talking about this” with zero proof—you’ve found content not worth your time.
Bullshit thrives where speed beats accuracy. Social media rewards bold claims, not careful analysis. By recognizing its hallmarks, you protect your attention from empty noise and focus on substance over show.
Social Media and Workplace Dynamics
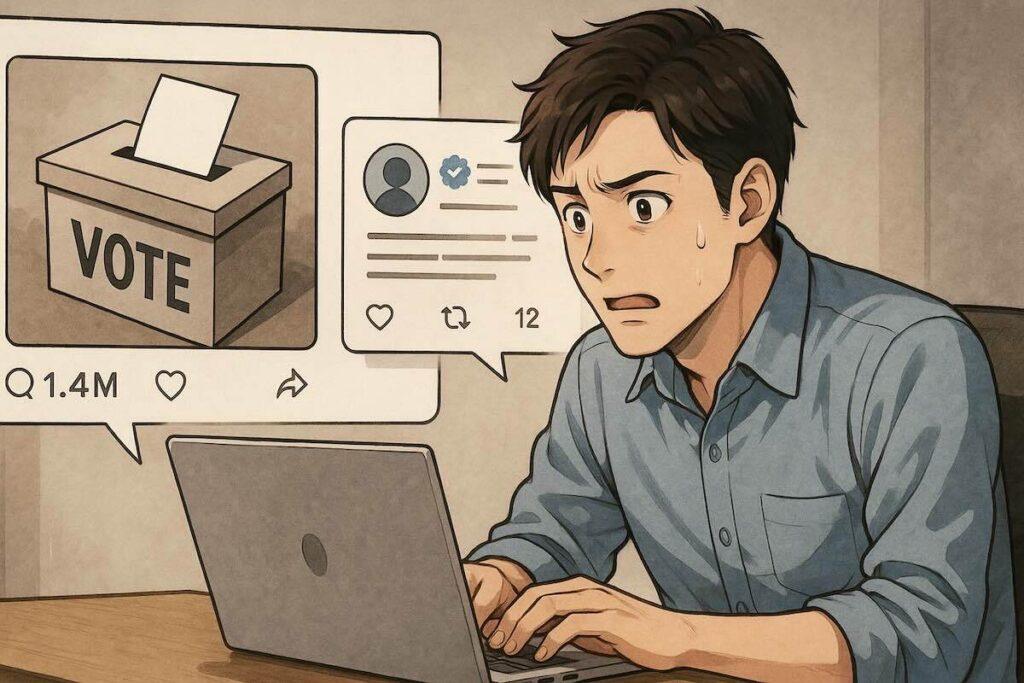
Picture this: A fabricated story about election fraud gains 1.4 million views overnight. Meanwhile, a detailed fact-check from verified sources gets 12 retweets. This imbalance shapes how people process information—online and at work.
Impact on X (Twitter) and False News Spreading
Research shows lies travel faster than truths. A 2018 MIT study found false claims spread six times quicker on X. During the 2016 U.S. election, one viral hoax reached more people than major news outlets combined. Corrections? They arrived late and underfunded—like showing up to a fire with a teacup of water.
Workplace Rumors and Their Effects on Productivity
Offline environments face similar problems. A baseless rumor about layoffs can slash productivity by 40% within hours. Employees spend time speculating instead of collaborating, which often leads to unnecessary arguments. In one survey, 38% reported workplace gossip directly harmed their job performance, creating a burden that distracts people from their goals.
These cases reveal a pattern. Quick claims thrive where speed beats accuracy. Whether battling viral myths or office whispers, focus energy on high-stakes data—not every spark needs extinguishing.
Addressing these questions can help maintain a productive environment.
Conclusion
The Brandolini Law mental model is more than a witty saying. It’s a vital tool for navigating today’s world filled with noise and misinformation. By grasping its roots, how it spreads, and its psychological effects, you can decide which fights are worth your time.
Whether you’re leading a team, handling a brand, or just scrolling through your feed, this concept is key. It helps you save energy and concentrate on what’s true. In a world where lies spread quickly, being able to tell fact from fiction is your strongest shield.


